Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed how businesses store data, run applications, and access computing power. At its core, cloud computing means using remote servers hosted on the internet to manage, store, and process data instead of relying on local servers or personal computers. This shift from traditional on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based services has enabled unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost savings across industries.
This guide explains what cloud computing is, how it works, the different models available, and what businesses should consider when getting started.

What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources over the internet instead of from servers located in your own office or data center. These resources can include servers, storage, networking, software, and analytics tools.
Traditionally, businesses purchased hardware, installed software locally, and managed everything in-house. Cloud computing shifts that responsibility to a service provider. Rather than owning the infrastructure, you access it as needed and pay for what you use.
It is important to understand that the cloud still relies on physical equipment. The difference is where that equipment lives and who manages it. Cloud providers operate large, secure data centers designed for performance, redundancy, and availability. Users connect to those systems through the internet.

How Cloud Computing Works
At a high level, cloud computing works by pooling computing resources and making them available on demand. Providers use virtualization technology to divide physical servers into multiple virtual environments. This allows resources to be allocated efficiently and scaled quickly.
When a business launches an application, stores data, or runs workloads in the cloud, those tasks are handled by servers in a provider’s data center. If demand increases, additional resources can be assigned automatically. If demand drops, resources can scale back.
This flexibility is one of the cloud’s biggest advantages. Businesses no longer need to overbuy hardware in anticipation of growth or risk downtime due to limited capacity.
Major providers like Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services operate global networks of data centers designed to deliver high availability and geographic redundancy.
The Three Main Types of Cloud Services
Not all cloud services work the same way. Most offerings fall into one of three categories.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service delivers applications over the internet. Users access the software through a browser or app without installing or maintaining it locally.
Common examples include email platforms, collaboration tools, customer relationship management systems, and file sharing services. Updates and security patches are handled by the provider, which reduces administrative overhead.
SaaS is often the first step into cloud computing because it requires minimal technical involvement and delivers immediate value.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service provides an environment for building, testing, and running applications. The provider manages the infrastructure and operating systems, while developers focus on the application itself.
PaaS is useful for organizations that want to create custom software without managing servers or worrying about maintenance. It supports faster development cycles and more consistent deployment.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service offers virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. Businesses have more control over how systems are configured, while the provider maintains the physical hardware.
IaaS is commonly used for migrating existing workloads to the cloud, supporting disaster recovery, or creating flexible environments that can grow over time.
Cloud Deployment Models Explained
Beyond service types, cloud computing also differs in how environments are deployed.
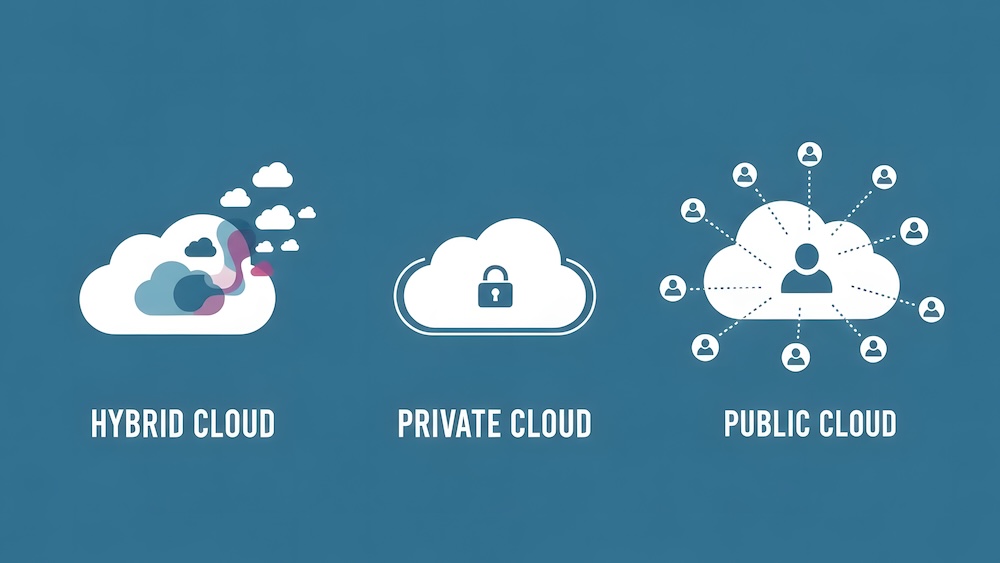
Public Cloud
Public cloud environments use shared infrastructure operated by a third-party provider. Multiple customers use the same underlying hardware, with strict logical separation.
A public cloud is cost-effective, scalable, and widely used for general business workloads such as collaboration tools, web applications, and development environments.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization. It may be hosted in a company-owned data center or managed by a third party.
Private cloud environments offer greater control and customization. They are often chosen by organizations with strict performance, data residency, or compliance requirements.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises systems with cloud resources. Some workloads remain local, while others run in public or private cloud environments.
This approach allows businesses to modernize gradually and place workloads where they make the most sense.
The Business Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing delivers advantages that go beyond technical convenience.
Scalability allows organizations to grow or adjust resources without purchasing new hardware. Cost structures shift away from large upfront investments toward predictable usage-based spending. Accessibility supports modern work environments by allowing teams to work securely from almost anywhere.
Cloud platforms also support business continuity. Built-in redundancy, backup options, and geographic distribution reduce the impact of outages and disasters.
Common Cloud Computing Use Cases
Cloud computing supports a wide range of business needs.
File storage and sharing enable teams to collaborate securely without relying on local servers. Backup and disaster recovery solutions protect data and improve recovery times. Business applications can be hosted in the cloud to improve availability and performance.
Development and testing environments are another common use case. Teams can spin up resources quickly and shut them down when no longer needed.
Is Cloud Computing Secure?
Security is one of the most common concerns about cloud computing. In practice, cloud providers invest heavily in protecting their environments through physical security, encryption, monitoring, and compliance certifications.
Security in the cloud follows a shared responsibility model. Providers secure the infrastructure, while businesses remain responsible for user access, data handling, and configuration.
When properly managed, cloud environments can be more secure than aging on-prem systems that lack regular updates or monitoring.

Getting Started with Cloud Computing
Many organizations begin with low-risk workloads such as email, file storage, or backup.
A thoughtful approach includes assessing current systems, identifying goals, and choosing the right deployment model. Working with a knowledgeable technology partner can help design an environment that aligns with business needs and long-term plans.
Cloud adoption works best when it is planned, not rushed.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cloud Computing
Is cloud computing only for large companies?
No. Cloud computing is widely used by small and mid-sized businesses because it reduces the need for large infrastructure investments.
Does moving to the cloud mean eliminating on-prem systems?
Not necessarily. Many organizations use hybrid cloud models that combine cloud services with existing infrastructure.
Is cloud computing expensive?
Costs vary depending on usage and design. Cloud computing often reduces hardware and maintenance costs, but proper planning is important to control spending.
Can cloud computing support compliance requirements?
Yes. Many cloud providers support compliance frameworks for healthcare, finance, and other regulated industries when environments are configured correctly.
Making Cloud Computing Work for Your Business
Cloud computing gives businesses the flexibility they often struggle to achieve with traditional infrastructure. Systems are easier to scale, recovery is built into the design, and teams are no longer constrained by hardware that cannot keep up. With the right planning and support, the cloud becomes a stable platform that evolves as the business does.
About Logista Solutions
Logista Solutions is a nationally recognized leader in a broad range of technology management solutions. As one of the largest technology support providers in the U.S., Logista provides innovative and holistic solutions to help companies take control of their IT infrastructure and achieve better business outcomes. Popular services include Managed IT as a Service, VoIP and Unified Communications, Managed Print, Cloud Services and Asset Disposition.



